Measurements Used to Describe Crystal Structures
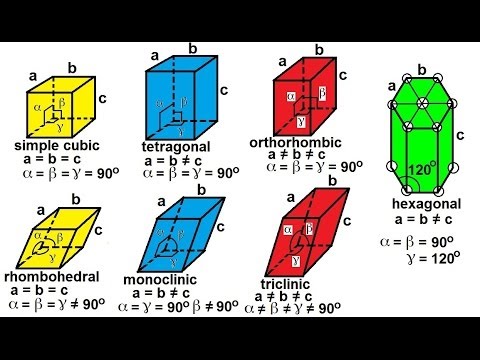
The combination of unit cell edge lengths a b c and inter-axial angles that defines the unit cell geometry alpha beta gamma crystal system. Crystal Structures of Some Common Binary Compounds We have now dealt with all of the possible cubic crystal structures for metals.
Chemistry Liquids And Solids 32 Of 59 Crystal Structure Seven Types Of Unit Cells Youtube
The geometry of the unit cell is defined as a parallelepiped providing six lattice parameters taken as the lengths of the cell edges a b c and the angles between them α β γ.

. The molecular and crystal structure of 3-nitropyrazole was determined by X-ray analysis. Basic info about minerals physical properties of minerals based on chemical composition and structure and importance of minerals. Rotating Crystal Method 3.
Atomic lattice or structure. A b c abg90ー a b c Note. A pinacoidalso called the parallelohedron is one of the forms in this crystallographic system.
Diffraction is the change in the direction of travel experienced by an electromagnetic wave when it encounters a physical barrier whose dimensions are comparable to those of the wavelength of. Its resistance to breaking crushing bending or tearing. Measurement is often considered a hallmark of the scientific enterprise and a privileged source of knowledge relative to qualitative modes of inquiry.
Resolution of smaller structures requires larger values of some combination of large scattering angles and short wavelenght of the incident light. The coordination number of each atom in the body-centered cubic structure is 8. Electron tomography is often an effective method used to reconstruct the 3D structure of nanoparticles from a single axis tilt series typically 75 to 75 of 2D STEM or TEM images.
Simple cubic crystal structure does not have an atom at the center of the unit cell or faces of the unit cell. The goniometer is used to position the crystal at selected. From the Fourier uncertainty principle.
Electrons are used to determine the structure of crystal surfaces. In this type of crystal structure one atom is situated at each corner of the unit cell as shown in the figure. Also known as the isometric system.
The unit cell is defined as the smallest repeating unit having the full symmetry of the crystal structure. The strength of a mineral. See the answer See the answer done loading.
To obtain an x-ray diffraction measurement three components are necessary. In the simple cubic crystal structure the total number of atoms is equal to eight. The atomic lattice is a three dimensional network of atoms that are arranged in a symmetrical pattern.
Terms commonly used to describe the tenacity of a mineral are brittle sectile malleable flexible elastic ductile and tough. To have diffraction the wavelength I of the electrons should be on the order of the lattice constant which is typically 030 nm. Crystal habit with the appearance of a paper tablet.
If any axis was of equal length to any other then we would be in the tetragonal system. Cube diamond fluorite pyrite. Based on a square inner structure.
Despite its ubiquity and importance there is little consensus among philosophers as to how to define. The triclinic unit cell contains 12 molecules which form four hydrogen-bonded NHN trimers. In some crystal healing practices the axial symmetry of a crystal is.
Laue Spot Method 2. Simple Cubic Crystal Structure SC. Measurement is an integral part of modern science as well as of engineering commerce and daily life.
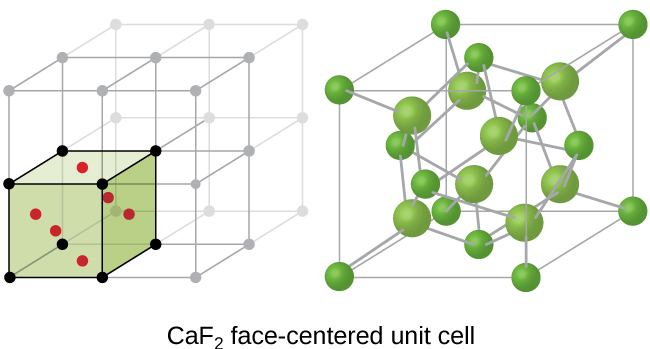
The atomic contents of the unit cell are a simple multiple Z of the composition of the material. It turns out that the structures of binary ionic compounds ie. In this method a single crystal specimen is held stationary in a beam of X-rays of continuous wavelength.
A crystal sample a source of x-ray beams and a detector. On the far left is the body-centered cubic bcc structure. Exhibit different strengths and ductilities.
Data from an X-ray crystallography experiment is used to generate a three-dimensional model of the molecules comprising the crystal. A scheme by which crystal structures are classified according to unit cell geometry which is specified by the relationships between the edge lengths and inter-axial angles. Experimental Determination of Crystal Structures 12 Phase Information is Lost.
Five forms 3 symmetry classes. X k π K i i K d e eK ρ ρ ρK r r Kr θ. The size of the unit cell and the arrangement of atoms in a crystal may be determined from measurements of the diffraction of X-rays by the crystal termed X-ray crystallography.
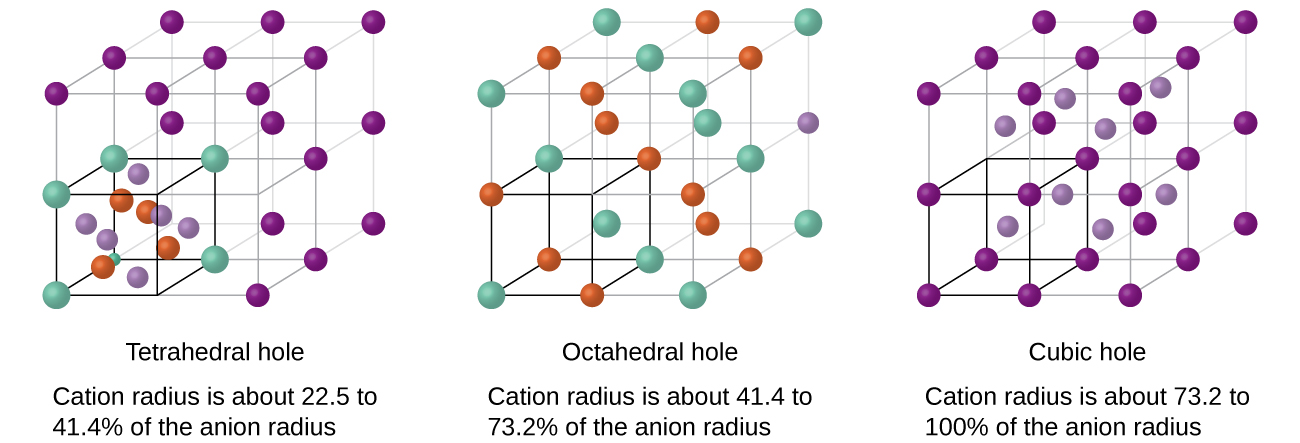
The following points highlight the three main methods for determination of crystal structure of materials. Most pure metals naturally adopt one of these three closest packing arrangements. The minimum amount of information needed to specify a crystal structure is the unit cell type ie cubic tetragonal etc the unit cell parameters and the positions of all of the atoms in the unit cell.
ExDullShiny Smooth flat surfaces with regular geometric outlines. Scientists knowledge of molecular shapes bond angles and lengths are all based on results from such. 21 Although this method can provide a real 3D representation of the crystal morphology disadvantages include the difficulty to align the projections of a tomography tilt to a common.
All three axes are of equal length and intersect at right angles. Crystal structure is described in terms of the geometry of arrangement of particles in the unit cell. Here we have outlined the basic atomic structure of the seven systems along with some common examples of each system.
Describe your understanding of why different crystal structures. Now up your study game with Learn mode. You just studied 27 terms.
X-ray crystal structures can also account for unusual electronic or elastic properties of a material shed light on chemical interactions and processes or serve as the basis for designing pharmaceuticals against diseases. MX where M is the cation and X is the anion in 11 stoichiometry are often related to these metal structures in a relatively simple way. One of the six crystal systems.
In that crystal metal atoms occupy the eight corners of a cube along with one atom in the very center. The shape of the lattice determines not only which crystal system the stone belongs to but all of its physical properties and appearance. In a single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurement a crystal is mounted on a goniometer.
Used to describe how mineral surfaces reflect light.

Chemistry Liquids And Solids 32 Of 59 Crystal Structure Seven Types Of Unit Cells Youtube

Crystal Definition Types Structure Facts Britannica

Crystal Definition Types Structure Facts Britannica

Unit Cell Lattice Parameters Cubic Structures Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Digital Metal Tube Rotameter Manufacturer Best Price Area Measurement Manufacturing Metal
10 6 Lattice Structures In Crystalline Solids Chemistry

Pin By Hudsonroland On Magnetite Mineral Project Unit Cell Crystal Structure Magnetite

Hexagonal System Definition Facts Britannica
10 6 Lattice Structures In Crystalline Solids Chemistry

Discuss The Crystal Structure Of Cscl Solid State Physical Chemistry Youtube

Tj X Ray Crystallography Is A Tool Used For Identifying The Atomic And Molecular Structure Of A Crystal I X Ray Crystallography Molecular Structure Molecular
Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials

Excited To Share The Latest Addition To My Etsy Shop Monoclinic Crystal Structure Gemstone Kit Monoclinic Cr Crystals And Gemstones Crystals White Gift Boxes

Tutorial Of Vesta Software For Creating Crystal Structures Youtube

Crystal Definition Types Structure Facts Britannica




Comments
Post a Comment